Advancements in Synthetic Fuels: A Sustainable Solution for the Automotive Industry
Introduction: Imagine a world where your love for high-performance engines doesn't contribute to environmental degradation. The automotive industry is making this dream a reality with the development of synthetic fuels, a clean and sustainable energy source. This article delves into the fascinating world of synthetic fuels to give you a clear understanding of their potential role in the future of motoring.
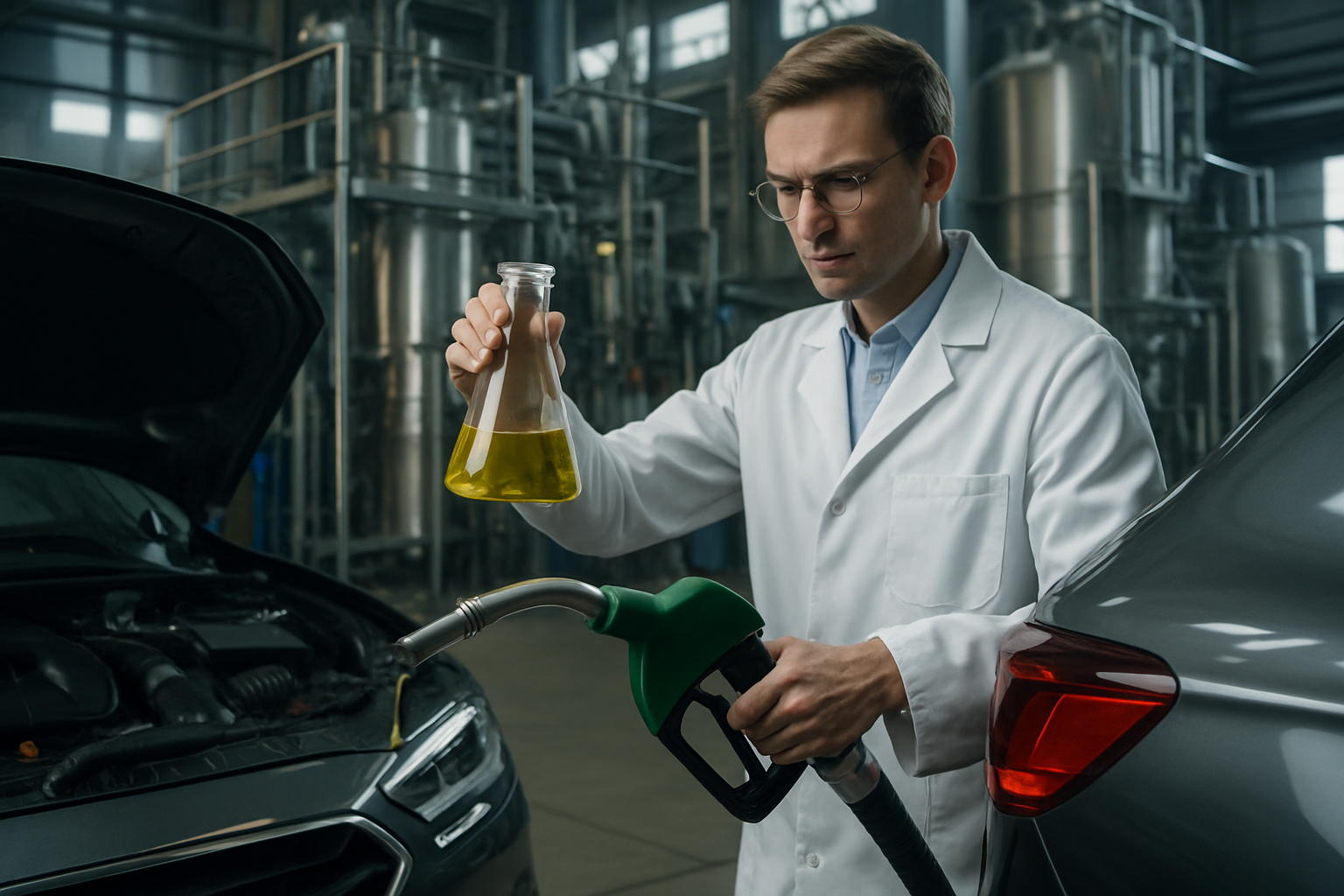

A Historical Overview of Synthetic Fuels
Synthetic fuels, also known as synfuels, are not a new concept. Their roots trace back to the 1920s when two German scientists, Franz Fischer and Hans Tropsch, developed a method to convert coal into liquid fuel. This method, famously known as the Fischer-Tropsch process, offered a solution to Germany’s oil shortage during World War II. However, the high production cost and availability of cheaper alternatives led to the decline of synfuel production post-war.
The Resurgence of Synthetic Fuels
Fast forward to the 21st century, and synthetic fuels are making a comeback. The looming climate crisis and the need for sustainable energy alternatives have revived interest in these lab-made fuels. Today, modern techniques allow the creation of synthetic fuels from a mixture of water, carbon dioxide, and electricity, making their production more environmentally friendly.
Current Trends in Synthetic Fuels
Major players in the automotive industry are investing in synthetic fuel research and development. Porsche, for instance, is building a pilot plant in Chile to produce synthetic fuel, while Audi has already started producing e-diesel, a type of synthetic fuel, at a research facility in Switzerland. These fuels are not only cleaner but also compatible with existing internal combustion engines, making them an attractive alternative to traditional fuels.
Impact of Synthetic Fuels on the Automotive Industry
The advent of synthetic fuels could revolutionize the automotive industry. It offers a way to keep internal combustion engines, particularly those in classic and sports cars, on the road without contributing to carbon emissions. Furthermore, synthetic fuels burn cleaner than their petroleum counterparts, reducing engine wear and increasing vehicle lifespan.
Challenges in Implementing Synthetic Fuels
While synthetic fuels hold great promise, their widespread adoption faces several hurdles. The cost of production, particularly the electricity required, is high. There are also concerns about the scalability of production and the potential competition with food production for arable land if biomass is used as a feedstock.
In conclusion, synthetic fuels present an exciting opportunity for the automotive industry. While challenges remain, their potential to maintain the joy of driving while contributing to a sustainable future makes them a technology worth watching. As we delve further into the 21st century, it’s clear that the automotive world is on the brink of significant change, and synthetic fuels could be a key player in this evolution.